VPD: The Key to Thriving Plants
Understanding Vapor Pressure Deficit (VPD) and Its Impact on Plant Health
When it comes to plant growth, there’s a delicate balance of environmental factors that play a crucial role in how plants absorb water and nutrients, grow, and even defend against disease. One of the most significant yet often overlooked factors is Vapor Pressure Deficit, or VPD. Knowing what VPD is and how to manage it can make a noticeable difference in plant health, growth rates, and yield quality. Here’s why VPD matters and how you can use it to optimize your growing environment.
What is Vapor Pressure Deficit (VPD)?
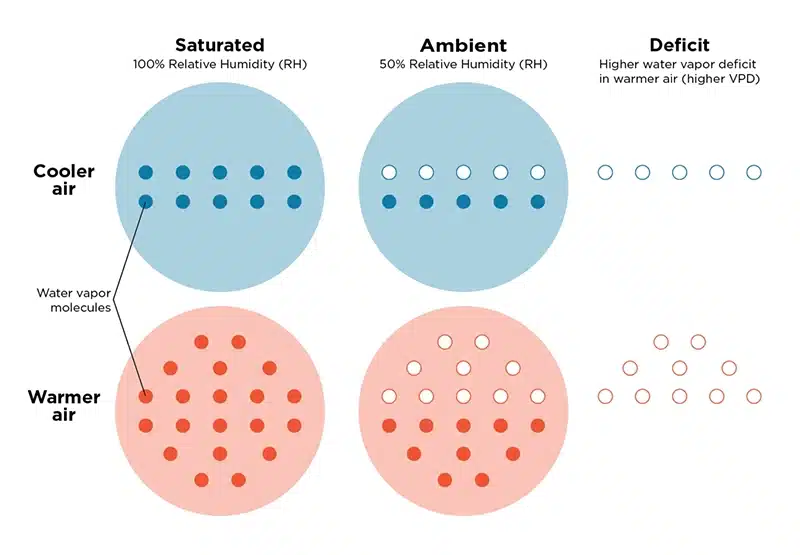
VPD is a measurement of the difference between the amount of moisture in the air and how much moisture the air can hold when it’s fully saturated. Essentially, it tells us how "thirsty" the air is. This “thirst” determines how readily water vapor leaves the plant’s leaves, a process known as transpiration.
- High VPD (when the air is very dry) means that the air pulls water from the plants more aggressively, causing them to lose moisture quickly.
- Low VPD (when the air is close to saturated) means that the air doesn’t draw water as effectively from the plants, reducing transpiration.
This balance affects how plants take up nutrients, grow, and respond to stresses in their environment.
Leaf and Room VPD: A Dynamic Balance
Leaf VPD and room VPD are interconnected concepts crucial for optimizing plant health and growth. Room VPD refers to the overall moisture conditions within the growing environment, influencing how much water vapor is present in the air. In contrast, leaf VPD specifically measures the moisture gradient between the inside of the leaf and the surrounding air.
A well-managed room VPD creates an ideal environment that allows for effective leaf VPD, promoting efficient transpiration and nutrient uptake. This balance between room and leaf VPD is essential for maximizing water uptake, enhancing nutrient transport, and improving the absorption of CO₂, all of which boost photosynthesis and increase yields. Understanding and managing both types of VPD are essential for fostering strong, resilient plants and ensuring successful growth.
Why VPD Matters for Plant Health
VPD directly influences a plant’s ability to transpire water. Transpiration is essential for nutrient uptake, temperature regulation, and overall growth. When VPD is optimal, plants can efficiently pull water from their roots through their vascular system and release it through small pores called stomata. This cycle not only delivers essential nutrients but also cools the plant and maintains internal water balance.
However, if VPD is too high or too low, problems can arise:
High VPD (Dry Conditions):
- When VPD is high, the air pulls water from the leaves more quickly. This can lead to excessive water loss from the plants, especially if the roots can’t keep up with the demand. Plants may wilt, their growth may slow, and they can become susceptible to stunted growth and nutrient deficiencies. In extreme cases, high VPD can also increase stress, making plants more vulnerable to disease.
Low VPD (Humid Conditions):
- When VPD is low, the air is saturated, and plants don’t lose water as quickly. While this might seem like a good thing, low VPD can prevent proper transpiration, leading to reduced nutrient uptake and slowing down the plant’s growth. Low VPD can also encourage mold, mildew, and other diseases to develop on plant surfaces, as there’s less air movement and moisture tends to linger.
Achieving the Optimal VPD
Each plant type has an ideal VPD range, often determined by species, age, and growth stage. Younger plants, for example, tend to do better with lower VPD because they are more sensitive to water loss, while mature plants can handle slightly higher VPD. By keeping VPD within the ideal range, you help plants grow more vigorously, with better nutrient uptake, healthier development, and resilience against environmental stressors.
Tips for Managing VPD in Your Growing Environment
Monitor Humidity and Temperature: Since VPD is a function of both humidity and temperature, you’ll want to keep an eye on both. Tools like hygrometers and digital thermometers can help you monitor these conditions accurately.
Adjust Humidity Levels: Use humidifiers or dehumidifiers to adjust the relative humidity. Keeping humidity within an optimal range ensures VPD stays balanced, reducing plant stress and enhancing growth.
Control Temperature: Managing temperature is equally important. High temperatures increase VPD, while low temperatures decrease it. Depending on your plants’ needs, consider using heaters or fans to adjust temperatures appropriately.
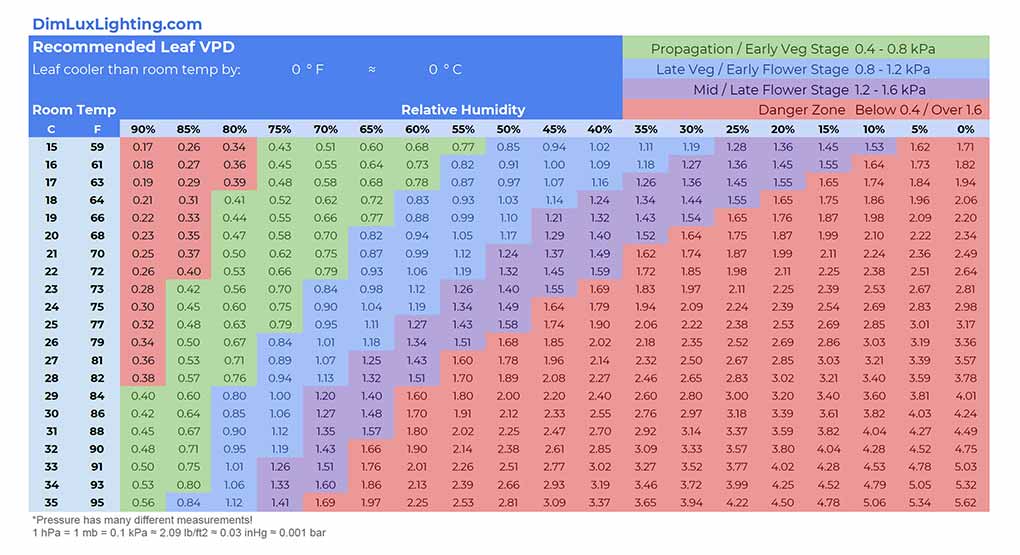
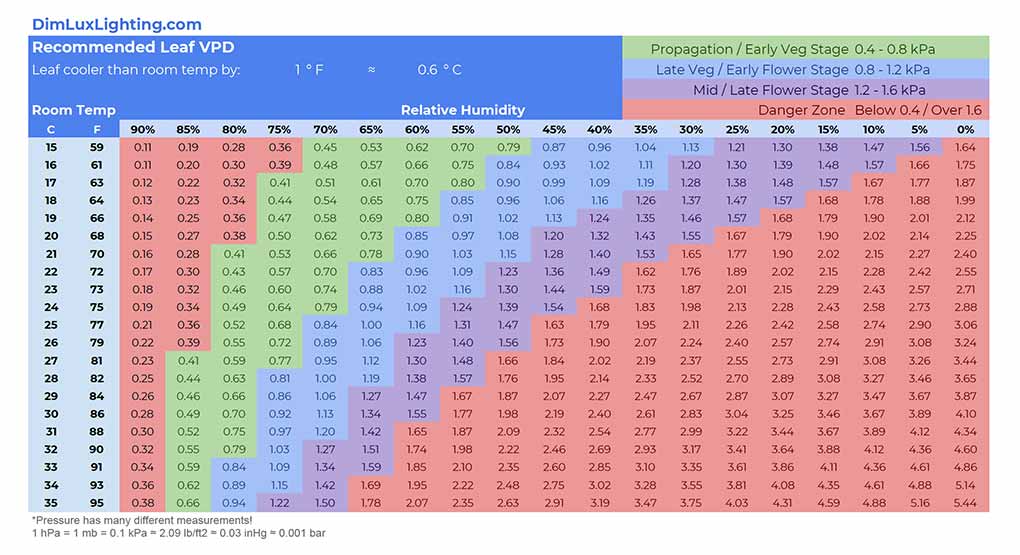
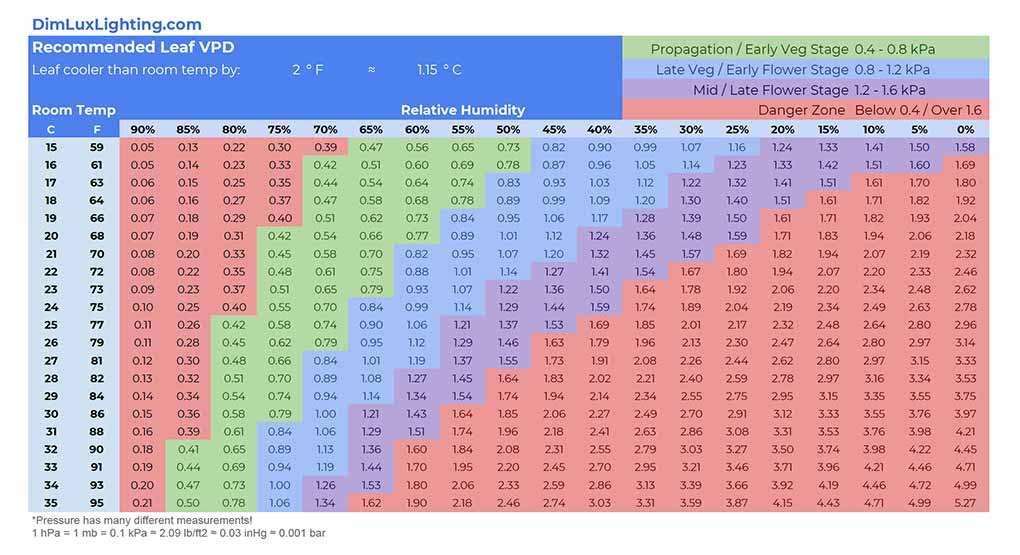
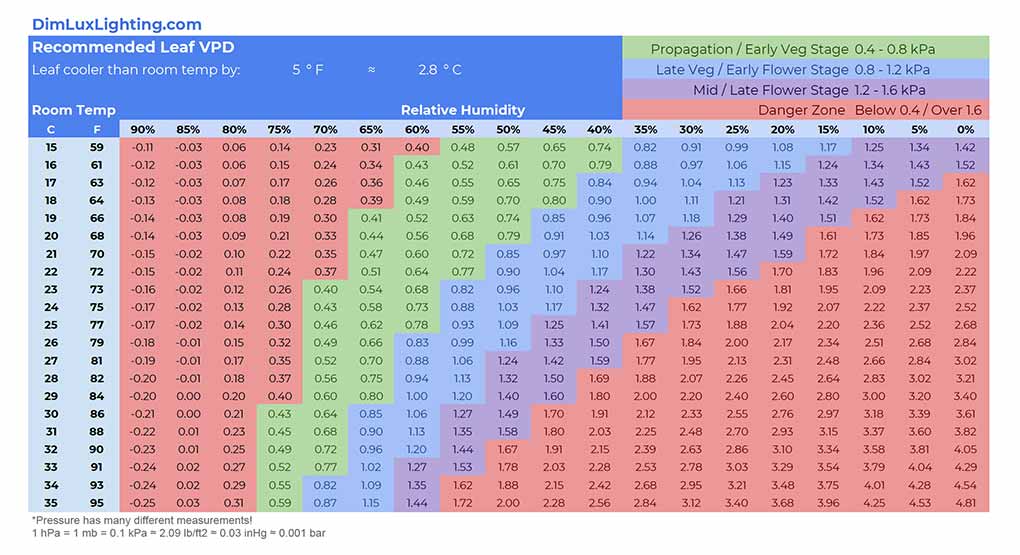
Use a VPD Chart: Many growers find VPD charts extremely helpful for achieving their target VPD. These charts map out the relationship between temperature and humidity to give you the optimal VPD for different stages of plant growth.
Utilize a VPD Calculator: To simplify calculations and adjustments, use an online VPD calculator. This tool lets you input your temperature and humidity levels to instantly find the VPD, making it easier to stay within the ideal range.
Benefits of Managing VPD
When you maintain the right VPD for your plants, you’re ensuring that they have the best possible conditions for:
- Efficient Water and Nutrient Uptake: Optimal VPD promotes balanced transpiration, which helps plants absorb the nutrients they need for healthy growth.
- Increased Growth Rates and Yields: With the right balance of moisture and temperature, plants can grow faster and produce better-quality yields.
- Improved Disease Resistance: Proper VPD management helps keep plants in a state of lower stress, which makes them less vulnerable to diseases caused by pathogens that thrive in overly humid conditions.
- Overall Health and Vitality: Plants grown in the right VPD range look healthier, with strong leaves, good structure, and vibrant colors.
Final Thoughts
Understanding and managing both room and leaf VPD is one of the most effective ways to ensure plants grow to their full potential. It goes beyond simply adjusting humidity or temperature alone, as VPD takes both factors into account. By keeping VPD in the ideal range, you’ll notice stronger, healthier plants that produce more consistent yields and can withstand environmental challenges. For any grower, VPD is a valuable metric that can make all the difference in plant performance and satisfaction with the results.
Here are some useful charts